Head Lice
Understanding Head Lice: What You Need to Know
Head lice are tiny parasitic insects that reside on the scalp and survive by feeding on human blood. These pests can cause significant itching and discomfort, making them a bothersome issue for those affected. Although head lice are an unpleasant nuisance, it's important to remember that they do not transmit diseases or lead to serious medical problems. However, due to their highly contagious nature, prompt treatment is essential to prevent their rapid spread within communities.
Effective Treatment and Management of Head Lice at Cumberland Skin
At Cumberland Skin, our dermatologists are well-equipped to assist patients dealing with head lice by offering effective treatment options tailored to each individual’s needs. We understand the urgency of addressing head lice and are here to provide comprehensive guidance on the most effective methods to eliminate these pests.Whether you're dealing with a head lice infestation or seeking preventive advice, our providers are dedicated to helping you manage and treat head lice efficiently. Don't let head lice disrupt your life—schedule an appointment with one of our experienced dermatologists at Cumberland Skin for expert care and support.
To learn more about head lice and the treatment options available, explore the detailed information below. Take control of your scalp health today by reaching out to our trusted providers.
Examples of Head Lice

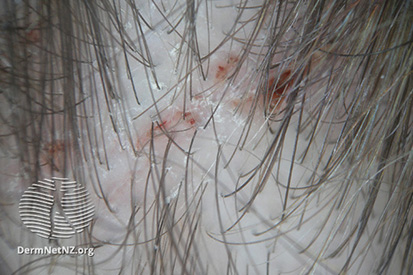



What are the Symptoms of Hair Lice?
- Discovering head lice typically begins with intense itching.
- You can identify tiny eggs resembling dandruff flakes in the hair before the onset of itching.
- To spot live eggs, closely examine the base of the hair, near the scalp, preferably under strong lighting conditions.
- Further signs may manifest as small, red bumps on the scalp, neck, or shoulders.
- Bumps may evolve into scaly patches or begin oozing.
Causes of Hair Lice
- Head lice is primarily transmitted from one person to another through direct physical contact.
- This easily transmissible infestation often occurs in close-knit environments, such as schools or households.
- The common mode of transmission involves lice crawling from the hair of an infected person to the hair of someone in close proximity.
How to Prevent Hair Lice
- Avoid Direct Head-to-Head Contact
- Educate About Personal Items: Stress the importance of not sharing personal items such as combs, brushes, hats, scarves, headphones, or any other items that come in contact with the hair.
- Regularly Clean Personal Items: Wash and clean personal items that come in contact with the hair, especially if they are shared among individuals.
- Use Protective Hairstyles: Keeping hair tied up or styled in a way that minimizes direct hair-to-hair contact.
- Routine Head Checks: Periodically check for signs of lice, such as itching, red bumps, or the presence of lice or eggs in the hair.
- Limit Personal Items in Shared Spaces: In communal spaces like schools or daycare centers, limit the sharing of personal items.
- Teach Proper Hygiene
- Be Informed: Stay informed about potential lice outbreaks in your community, especially if you have children in school.
Head Lice FAQs
Yes, dermatologists can effectively diagnose and treat head lice. They may recommend specific medicated shampoos, lotions, or prescription medications designed to eliminate lice.
Dermatologists may prescribe medications containing permethrin, pyrethrin, or malathion, which are designed to kill head lice and their eggs. The choice of medication depends on factors such as the patient's age, health, and any known sensitivities.
Head lice cannot survive for an extended period away from the scalp. They rely on human blood for nourishment. Items like hats, brushes, or bedding may be potential sources of transmission but are not long-term habitats for lice.
After undergoing effective treatment and ensuring that no live lice are present, individuals can typically return to school or work. It's important to follow school or workplace guidelines, which may vary.
From Our QualDerm Family of Brands: Back-to-School Exams
How to Treat Hair Lice
Your dermatologists can assist with head lice by providing guidance on effective treatments and helping manage potential complications. In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary. Additionally, dermatologists can provide support and address any skin-related issues that may arise due to scratching or irritation caused by head lice.
Related Blog Posts
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Learn more about the most common types of skin lesions we see at Cumberland Skin and how our dermatologists remove them.
Read More
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Preparing for your first dermatology appointment is important because it ensures everything goes as smoothly as possible and that your doctor is up-to-date on the status of your overall health and wellbeing. Here are our expert tips.
Read More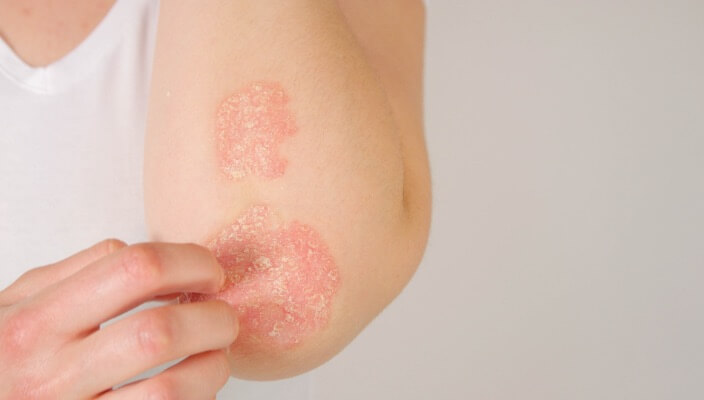
- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Learn the differences between dry skin, eczema, and psoriasis, their distinct characteristics, and potential triggers. Gain valuable insights into identifying symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment to effectively managing these common skin conditions.
Read MoreFeatured Products

CLn Healthy Scalp Shampoo
CLn Shampoo includes salicylic acid and sodium hypochlorite, and is designed for flakey scalps. It is an effective shampoo for normal-to-oily scalp and skin. Designed for scalp and skin prone to folliculitis, dermatitis, dandruff, beard dandruff and acne. 12 fl oz / 354 mL

SEEN Shampoo Fragrance Free
This award-winning sulfate free shampoo provides a luxurious lather that rinses easily without leaving the hair or scalp feeling stripped. When used as a regimen, SEEN products deliver stronger, smoother, healthier-looking hair. Developed specifically to be safe for sensitive, acne-prone, and eczema-prone skin. 8.6 oz Ingredients: Water, Sodium Lauroyl Methyl Isethionate, Cocamidopropylamine Oxide, Glycerin, Acrylates Copolymer, Glycol Distearate, Trisodium Ethylenediamine Disuccinate, C13-15 Alkane (plant derived), Guar Hydroxypropyltrimonium Chloride, Polyquaternium-7, Bisabolol, Citric Acid, Disodium Edta, Phenoxyethanol, Ethylhexylglycerin, Aminomethyl Propanol, Sodium Hydroxide, Tocopherol, Sodium Benzoate


